TES µEngine - Overview
TES µEngine provides a processor tailored precisely to your needs. Instead of implementing complex state machines in hardware, they are represented in software. The µEngine executes this software – highly specialized, efficient, and with deterministic timing.
How does it work?
- Break down complex tasks into smaller subtasks.
- Each subtask runs on a dedicated µEngine.
- Multiple µEngines operate in parallel within the RAISE system, sharing resources and communicating seamlessly.
- The entire system can be cycle-accurately simulated on a PC, enabling precise runtime prediction.
RAISE System
The RAISE system (Related Array of Independent Single-tasking µEngines) supports the parallel execution of different tasks, enabling the efficient implementation of complex operations. Each µEngine can be optimized for its specific function and disabled when not needed to save power.
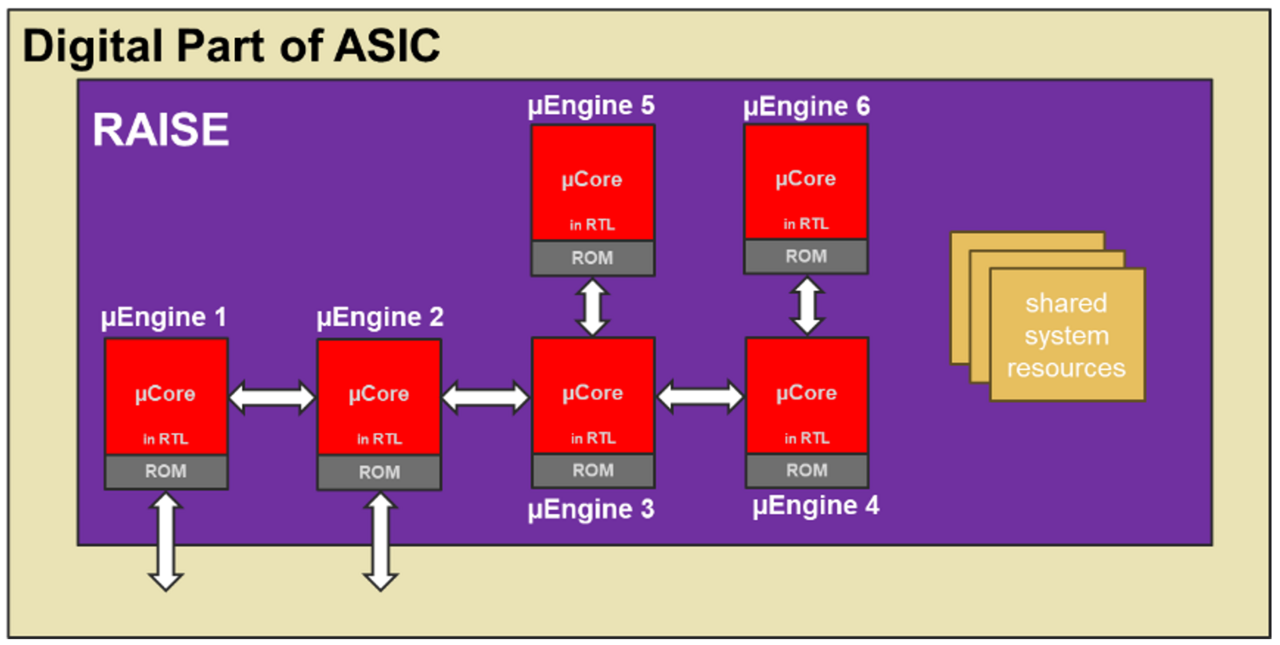
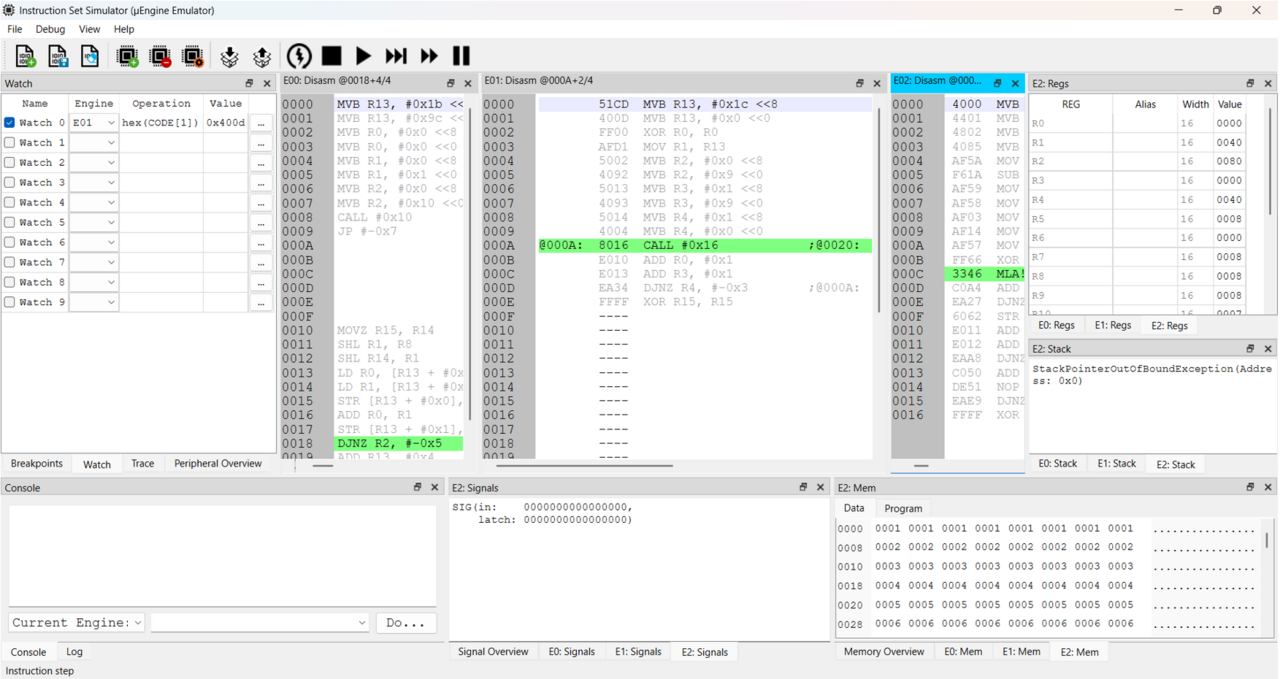
An entire RAISE system with multiple µEngines operating in parallel, can be cycle-accurately simulated on a PC, ensuring predictable runtime and avoiding hardware dependency during early development.
SCQA
Situation
ASIC development is becoming increasingly complex, with rising demands for flexibility, faster time-to-market, and IP protection. At the same time, development budgets and timelines are shrinking. Many companies face the challenge of implementing specialized functionality in hardware without having in-house ASIC expertise.
Complication
Traditional ASIC designs are rigid, simulation-intensive, and tightly coupled to hardware availability. Software development often starts late in the process. Any change in system behavior requires RTL modifications and full re-verification. Furthermore, proprietary IP must often be disclosed, posing a risk to sensitive algorithms.
Question
How can an ASIC be developed that is modular and scalable, enables early software development, protects IP, and reduces verification effort and time-to-market?
Answer
RAISE – Related Array of Independent Single-threaded µEngines – is a modular, software-defined ASIC architecture featuring:
- Configurable µEngines (CPU + RAM + ROM + optional peripherals)
- ROM-based software control (no RTL changes for behavior updates)
- Cycle-accurate simulation on PC (software development before tape-out)
- IP protection via encrypted RTL integration
- Flexible service models (Turn-Key or Joint Development)
RAISE enables parallel development, deterministic behavior, and scalable architecture – ideal for safety-critical, time-sensitive, or IP-sensitive applications.
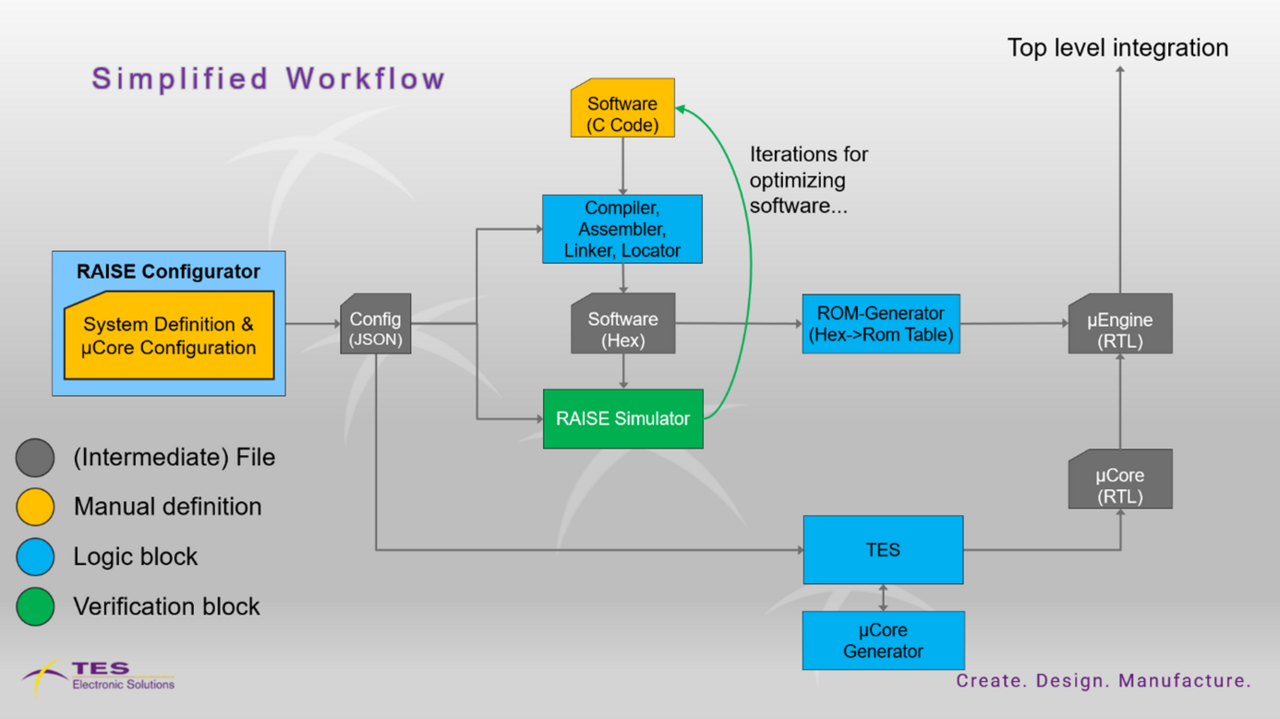
µEngine Ecosystem
- RAISE CONFIGURATOR
- To configure the various µCores that make up the µEngines
- To configure the various µEngines and peripherals that make up the µSystem
- To create a configuration file shared by simulator, assembler and C compiler
- RAISE SIMULATOR
- To simulate several configured µEngines in parallel as a µSystem
- To execute and debug programs for the configured µEngines in the simulated µSystem
- µEngine Assembler
- To convert program code in µCore assembler mnemonics to binary machine code for ROM masks
- µEngine C-Compiler
- To convert program code to µCore assembler mnemonics
- Linker, Locator, Binutils
For More Information
Please contact sales@tes-dst.com.

